The Animals
Bengal Tiger
General Info
Common Name: Bengal Tiger
Scientific Name: Panthera tigris tigris
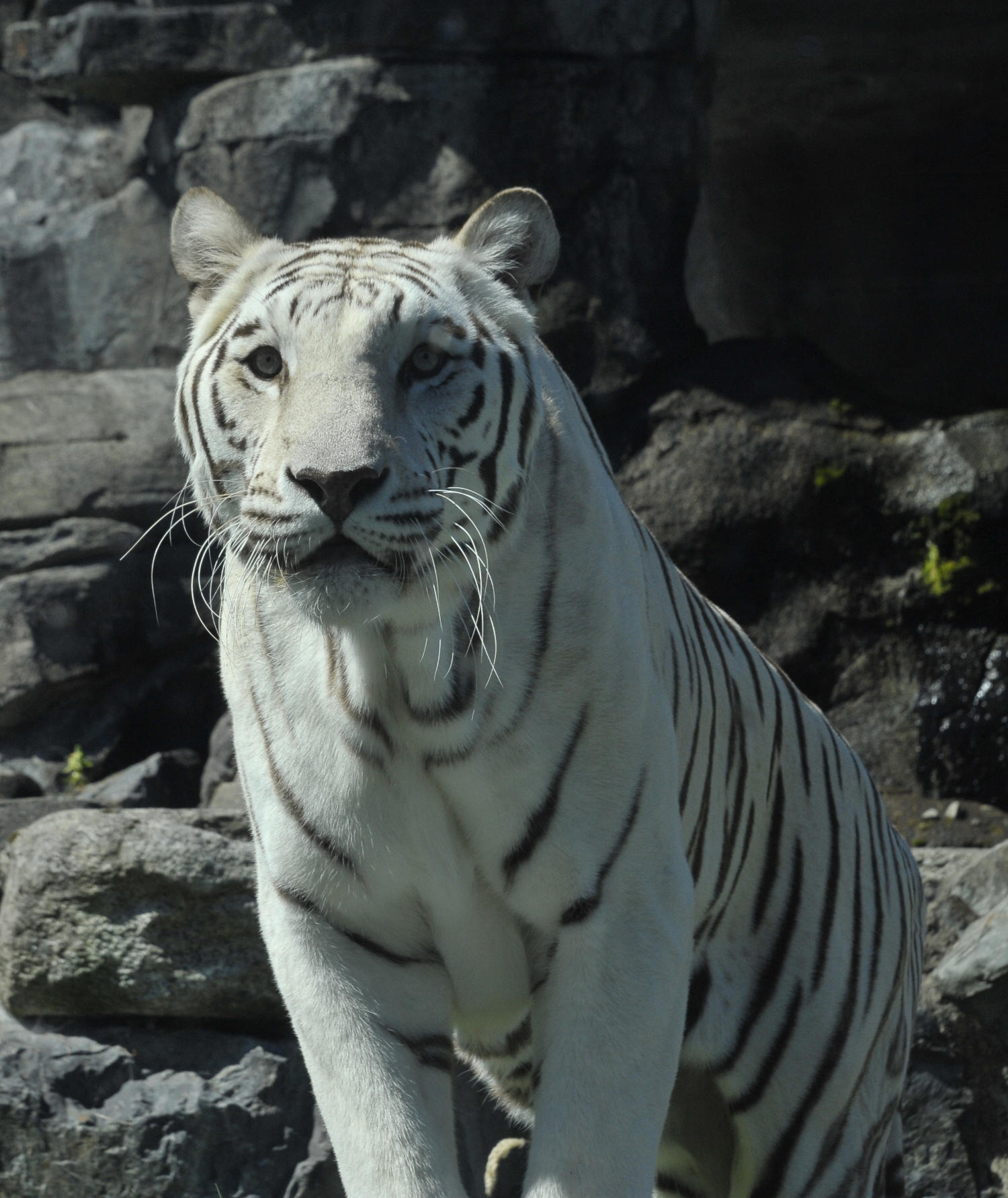
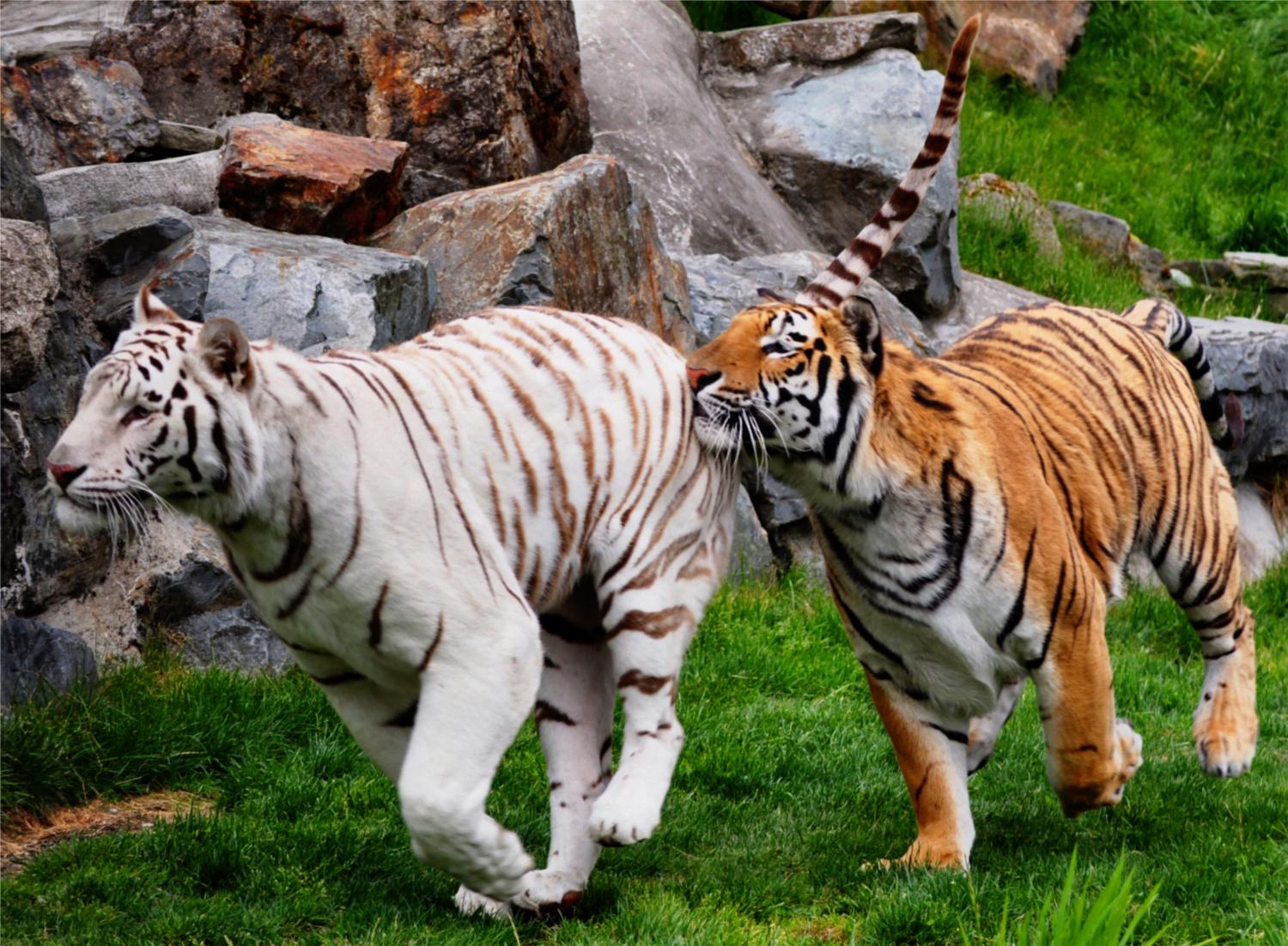
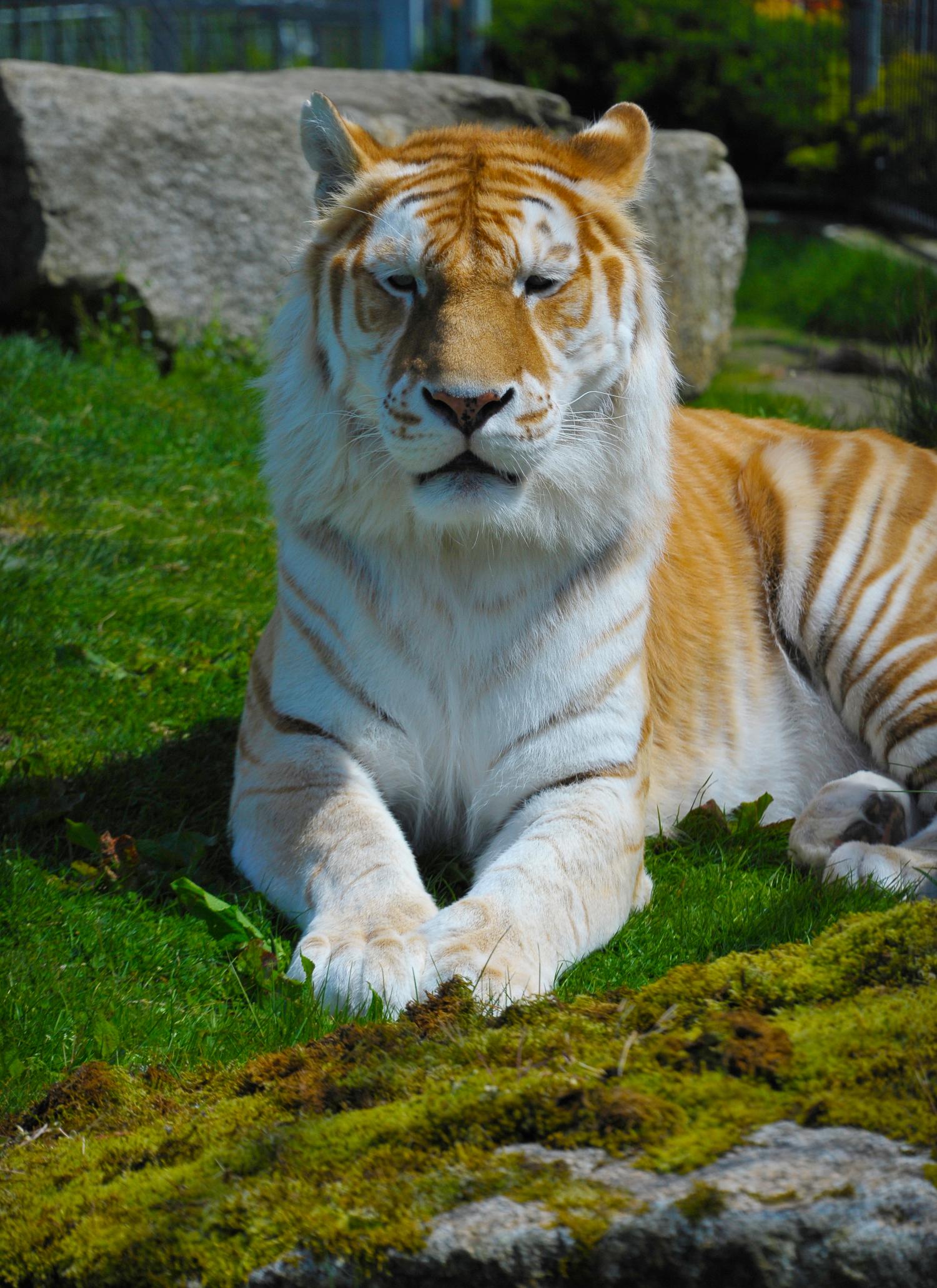
Physical Appearance: Dominant coat coloration of a Bengal Tiger is orange, white ventral area, and stripes that can vary from brown to black with amber-colored eyes. The form and density of the stripes differ between populations, but most tigers have over 100 stripes. White tigers arise from a naturally occurring recessive variation that produces blue eyes and chocolate-colored stripes on white background. There are two other color variants that can occur, but the probability is low.
Length/Weight: Males average 9-10 feet and females average 7-8 feet, from nose to tail, males range between 400-570+ lbs.; females 220-350+ lbs.
Lifespan: 8-10 years in the wild, up to 20 years in captivity

Environment
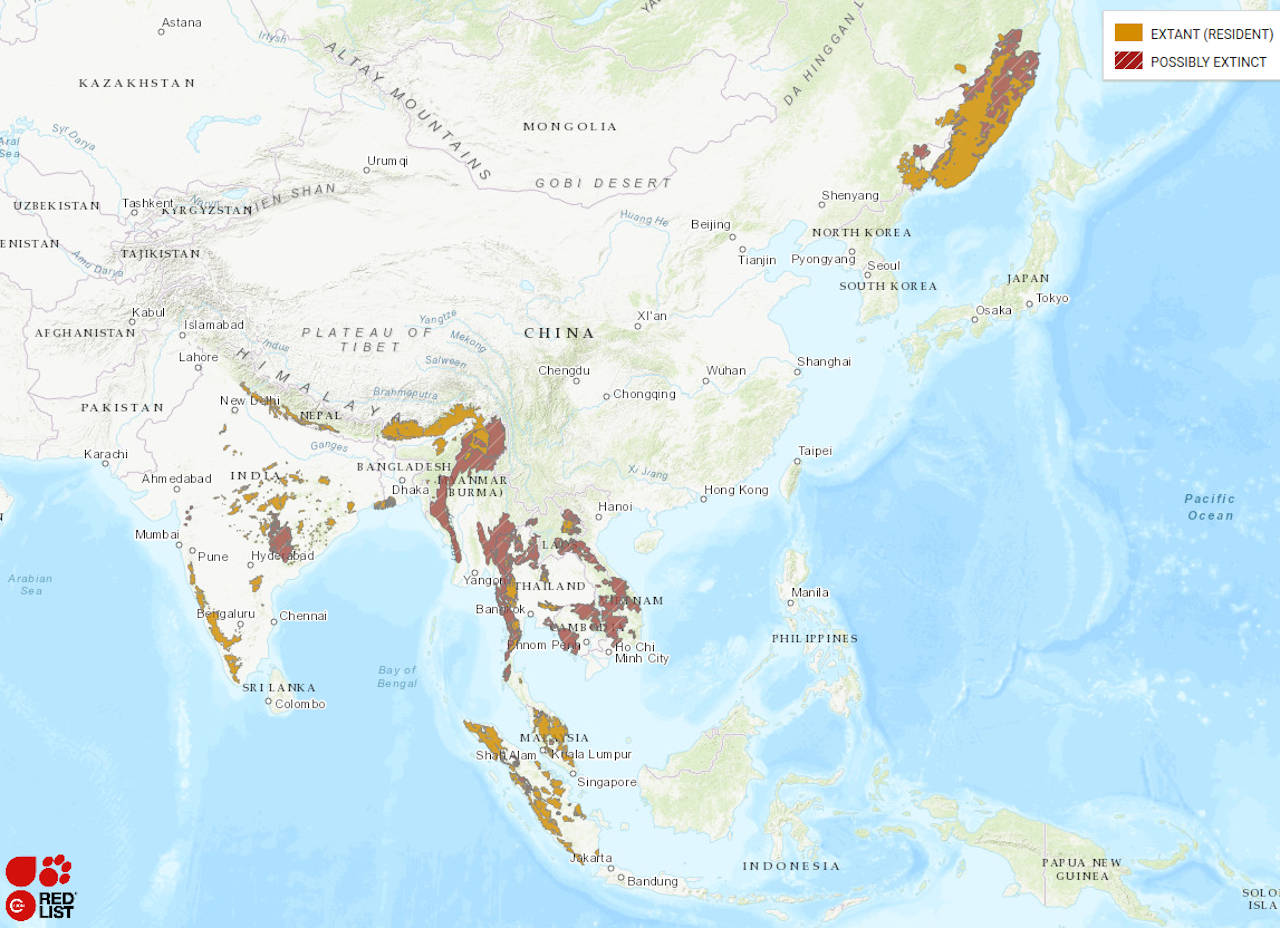
Range: The Bengal tiger is found in India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and Burma.
Habitat: Habitats vary from grasslands to subtropical and tropical rainforests, scrub forests, wet and dry deciduous forests, and mangroves
Diet
Tigers are hypercarnivores. Their main diet consists of large ungulates (water buffalo, gaur, chital, sambar, wild boar, etc.), but have been known to take smaller prey (hares, porcupines, primates, small carnivores, etc.), and rare occasions, crocodiles. Tigers have been known to take down prey weighing over 2,000 lbs., nearly 4-5x their body weight. A full-grown wild tiger has been recorded to eat upwards of 80 lbs. of prey in one sitting. What they do not finish will be cached to consume later.

Reproduction
Aseasonal over most of their territory. Gestation averages between 103-105 days, resulting in litters of two to five cubs. Cubs are about two pounds when born. The cubs are independent around 18 months of age and leave their mother around two years old. Females often inherit part of their mother’s range, while males disperse further away. Males and females are sexually mature between 2.5-3 years of age, yet the earliest breeding for females is 3 years old while males are 4 to 5 years old.

Conservation
Status:
Listed on IUCN: ENDANGERED
Population Trend: DECREASING
Efforts:
Threatened by habitat destruction and illegal poaching. Goal of worldwide efforts is to effectively double the tiger population known in 2010. This is being done by managing current habitat, eradicating poaching, engagement with the community, and restoring parts of their former range. Listed on CITES Appendix I.

Important Facts

A tiger’s roar can be heard up to 2 miles away.
Tigers will seek out water during high temperatures and can swim well. They have been observed to catch prey in the water.
Every tiger has its own distinct stripping pattern. Researchers have been utilizing this feature in order to accurately catalog wild tigers using remote trap camera systems.
Sources:
IUCN: RED LIST
Carnivores of the World: SECOND EDITION
Walker’s CARNIVORES of the World
National Geographic



